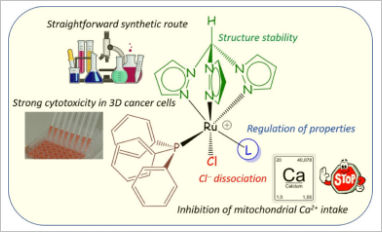
 Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Alberto Gobbo for his scientific publication entitled “Ruthenium (II)–Tris-pyrazolylmethane Complexes Inhibit Cancer Cell Growth by Disrupting Mitochondrial Calcium Homeostasis” in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Studies on the medicinal potential of ruthenium complexes containing a tridentate tris(1-pyrazolyl)methane ligand are almost absent in the literature. A straightforward route to access a family of novel, robust and water-soluble cationic ruthenium(II)–tpm complexes was developed. One key ligand modulates both the amphiphilic character and the strength of the ruthenium–chloride bond, which may be implicated in the activation mechanism.
Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Alberto Gobbo for his scientific publication entitled “Ruthenium (II)–Tris-pyrazolylmethane Complexes Inhibit Cancer Cell Growth by Disrupting Mitochondrial Calcium Homeostasis” in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. Studies on the medicinal potential of ruthenium complexes containing a tridentate tris(1-pyrazolyl)methane ligand are almost absent in the literature. A straightforward route to access a family of novel, robust and water-soluble cationic ruthenium(II)–tpm complexes was developed. One key ligand modulates both the amphiphilic character and the strength of the ruthenium–chloride bond, which may be implicated in the activation mechanism.
 Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Andrea Taddeucci for winning one of the poster prizes at CD2022, an event organized by "New York University" (NYU) in New York. The title of his poster was "Circular Dichroism Imaging of Novel Chiral Organic Dyes in Thin Film using Diamond Light Source B23 highly collimated Synchrotron Radiation". Thin films of chiral dyes with semiconductive properties open the way to the fabrication of new generation optoelectronic devices with enhanced performances, thanks to the emission of circularly polarized light and the control of electrons' spin. Circular Dichroism (CD) Imaging technique provides preliminary information on the possibility to adopt them in the mentioned devices.
Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Andrea Taddeucci for winning one of the poster prizes at CD2022, an event organized by "New York University" (NYU) in New York. The title of his poster was "Circular Dichroism Imaging of Novel Chiral Organic Dyes in Thin Film using Diamond Light Source B23 highly collimated Synchrotron Radiation". Thin films of chiral dyes with semiconductive properties open the way to the fabrication of new generation optoelectronic devices with enhanced performances, thanks to the emission of circularly polarized light and the control of electrons' spin. Circular Dichroism (CD) Imaging technique provides preliminary information on the possibility to adopt them in the mentioned devices.
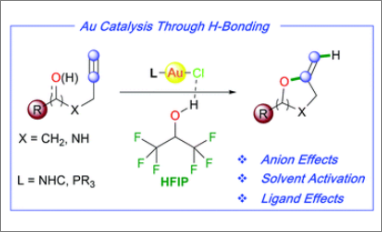 Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Alberto Gobbo for his scientific publication entitled “Hydrogen bonding-enabled gold catalysis: ligand effects in gold-catalyzed cycloisomerizations in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP)” in ChemComm. Gold catalysis has witnessed immense evolution in recent years, yet it still requires the use of activators to render the common AuCl(L)] complexes catalytically active. Herein, the H-bonding donor properties of hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) are utilized for Au–Cl bond activation and the ancillary ligand and counteranion effects on cycloisomerization reactions are showcased in HFIP as solvent. In addition, HFIP is not only a suitable solvent for gold catalysis with [AuCl(L)] complexes, but it also enables catalysis with Brønsted-basic complexes.
Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Alberto Gobbo for his scientific publication entitled “Hydrogen bonding-enabled gold catalysis: ligand effects in gold-catalyzed cycloisomerizations in hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP)” in ChemComm. Gold catalysis has witnessed immense evolution in recent years, yet it still requires the use of activators to render the common AuCl(L)] complexes catalytically active. Herein, the H-bonding donor properties of hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP) are utilized for Au–Cl bond activation and the ancillary ligand and counteranion effects on cycloisomerization reactions are showcased in HFIP as solvent. In addition, HFIP is not only a suitable solvent for gold catalysis with [AuCl(L)] complexes, but it also enables catalysis with Brønsted-basic complexes.
 Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Francesca Niccolai for winning one of the best presentations at Macrogiovani 2022, an event organized by "Associazione Italiana di Scienze e Tecnologie delle Macromolecole" (AIM) in Florence. The title of her presentation was "Next-generation composite polymeric membranes for semi-organic redox flow batteries". Redox flow batteries (RFBs) are promising candidates for large-scale energy storage thanks to their long service lifetimes, relatively low capital costs, and independent scaling of energy and power density. The membrane is a pivotal component of RFBs as it determines the performance as well as the economic viability of the batteries.
Congratulations to our Ph.D. student Francesca Niccolai for winning one of the best presentations at Macrogiovani 2022, an event organized by "Associazione Italiana di Scienze e Tecnologie delle Macromolecole" (AIM) in Florence. The title of her presentation was "Next-generation composite polymeric membranes for semi-organic redox flow batteries". Redox flow batteries (RFBs) are promising candidates for large-scale energy storage thanks to their long service lifetimes, relatively low capital costs, and independent scaling of energy and power density. The membrane is a pivotal component of RFBs as it determines the performance as well as the economic viability of the batteries.



