 Congratulations to our PhD candidate Andrea Volpe for his work entitled “Influence of cations size and charge on Zn electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents” published on the international journal Electrochimica Acta. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) are liquid mixtures exhibiting tunable physicochemical properties as a function of the nature and ratio of their components.
Congratulations to our PhD candidate Andrea Volpe for his work entitled “Influence of cations size and charge on Zn electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents” published on the international journal Electrochimica Acta. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) are liquid mixtures exhibiting tunable physicochemical properties as a function of the nature and ratio of their components.
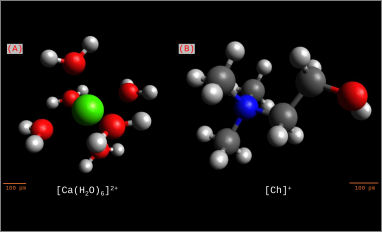
In this study, two DESs consisting of choline chloride or calcium chloride with ethylene glycol (CaDES1-2 and Ethaline, respectively) were tested in zinc electrodeposition experiments. These systems have different cations but otherwise similar composition; nonetheless their deposition processes are completely opposite, demonstrating that supposedly inert cations play a determining role. Zn deposition was fully reversible from CaDES1-2 even at low concentrations (0.1 M), while no deposition was obtained from Ethaline below 0.4 M. To understand the reason for this different behaviour, the systems have been studied by cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to obtain information on the double layer structure at the electrode/electrolyte interface. CaDES1-2 displayed lower differential capacitance values at negative potentials compared to Ethaline, suggesting thinner and less compact electrical double layer(s) at the electrode/electrolyte interface for CaDES1-2 compared to Ethaline. The nucleation mechanism of Zn from the calcium-based system and the morphology and elemental composition of the metallic coatings obtained were also characterized.
The paper is available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2025.148002


